
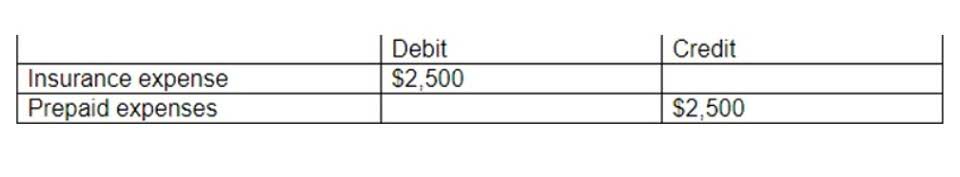
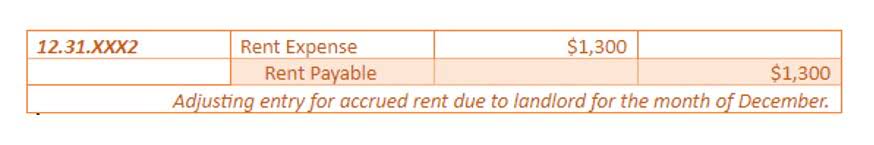
Learn more about how to forge a path to success in your accounts payable processes. Here’s https://meihealthcares.com/eft-payment-meaning-what-is-an-electronic-funds/ everything you need to know, including how to calculate the times interest earned ratio. If a company has a low times interest earned ratio, it can improve this measure by increasing earnings or by paying off debt. Cost-cutting can be an effective way to increase earnings, even if sales are not expanding.
AccountingTools
The times interest earned ratio, also known as the interest coverage ratio, is a metric that indicates a company’s ability to pay its interest obligations. It is determined by dividing the earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by the company’s total interest expense. A high TIE ratio indicates that a company generates enough operating income to comfortably cover its interest expenses, reflecting strong financial health and lower risk of default. It reassures lenders and investors about the company’s ability to meet debt obligations. The times interest earned ratio measures a company’s ability to meet its debt obligations by comparing earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) to interest expense. A higher TIE ratio indicates stronger financial health and a lower risk of default.
The Significance of Times Interest Earned in Financial Analysis
- A higher ratio suggests that the company is more likely to be able to meet its interest obligations, reducing the risk of default.
- Investors and analysts use this ratio, along with a range of other financial ratios, to paint a broader picture of a company’s current and future economic health.
- The TIE ratio is just one of many useful metrics used to evaluate financial health.
- When EBIT drops and interest costs rise, the TIE ratio declines, even if the business was previously in a strong position.
- These automatic ratio calculations could include the times interest earned ratio (which may be called interest coverage ratio) from the company’s income statement data.
- Yes, the TIE ratio can change depending on a company’s EBIT and interest expenses.
- It’s a vital component of a company’s financial statements, allowing for more informed decisions.
Luckily, I switched to Moon Invoice and found the hassles of stock and expense management getting faded. Discover top construction apps that can streamline workflow, improve project management, and boost productivity. The following section provides examples highlighting different scenarios you may encounter when calculating TIE ratios for your business. The argument for counting them is that they do tell you something about the company’s credit quality and ability to raise additional Debt. “Reasonable” and “targeted” levels vary by industry and company stage, but in most cases, a TIE in the 4 – 5x range is healthy and indicates that the company can easily service its Debt. As a point of reference, most lending institutions consider a time interest earned ratio of 1.5 as the minimum for any new borrowing.

Common Misconceptions About the TIE Ratio
The EBITDA coverage ratio indicates the company’s ability to pay interest based on cash flow from operations. Whether it’s the way the industry operates, economic recessions, technological advances, or changes in consumer trends, these outside issues need to be considered when analyzing a company’s finances. Comparing the ratio to other similar companies within your industry may help determine how you are positioned within the current economic landscape. It is a basic indicator of the company’s ability to pay off interest expenses, but it doesn’t account for principal repayments or other non-interest financial operations. It is also sensitive to interest rate fluctuations and debt levels, and may not accurately reflect a seasonal or cyclical company’s actual ability to consistently pay interest over the entire year. Every company is unique in its operating expenses, debt levels, earnings stability, capital structure, and more.
Times interest earned ratio formula
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Mat brings nearly a decade of experience from Shopify building financial documentation and public-facing content.
Income statements are also known as profit and loss (P&L) statements or earnings statements. It’s a critical financial statement that provides insight into a company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, and net income over an accounting period (usually a quarter or a year). Analysts and investors use income statements to evaluate how well a company generates earnings and pays off debt on time. The debt service coverage ratio determines if a company can pay all interest and principal payments (also called debt service). The Times Interest Earned (TIE) ratio measures a company’s ability to meet its debt obligations on a periodic basis. This ratio can be calculated by dividing a company’s EBIT by its periodic interest expense.
Debt Service Coverage Ratio & Financial Analysis
Alfalfa Mining Company went through a capital restructuring recently where they issued new stock and used the proceeds to pay off some notes payable and long-term debt. A very low TIE ratio suggests that the company may struggle to meet its interest payments. This can lead to financial distress, higher borrowing costs, or even bankruptcy if not addressed. Return on Assets (ROA) is times interest earned ratio a profitability ratio that measures how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate profit.
Debt Ratio: Definition, Formula (+ Free Calculator)
It covers preferred dividends, lease payments, and scheduled principal repayments. The primary purpose of the fixed charge coverage ratio is to provide a more comprehensive assessment of the company’s capacity to meet all its fixed financial obligations fully. In some respects the times interest ratio is considered a solvency ratio because it measures a firm’s ability to make interest and debt service payments. Since these interest payments are usually made on a long-term basis, they are often treated as an ongoing, fixed expense.
How to improve the times interest earned ratio
This indicates that Harry’s is managing its creditworthiness well, as it is continually able to increase its profitability without taking on additional debt. If Harry’s needs to fund a major project https://www.bookstime.com/ to expand its business, it can viably consider financing it with debt rather than equity. The TIE’s main purpose is to help quantify a company’s probability of default. This, in turn, helps determine relevant debt parameters such as the appropriate interest rate to be charged or the amount of debt that a company can safely take on.



